
Headaches are a menace that at some time or the other, has affected each one of us. Although contact with a headache sufferer will not produce a head ache in another, headaches are definitely a social problem that needs to be addressed.
Headaches affect so many people in such varying degrees that statistics are hard to compile. Headaches also appear to strike almost at will! It appears to the sufferer that elements of the metabolic, muscular, neural and vascular system cooperate magnificently to produce the torment of a headache; the causes behind a headache cannot always be immediately traced. This is because these are the results of subtle organic and psychic processes that are not always felt by the victim or instantly observed by the physician. However, there are some common reasons that underline most headaches.
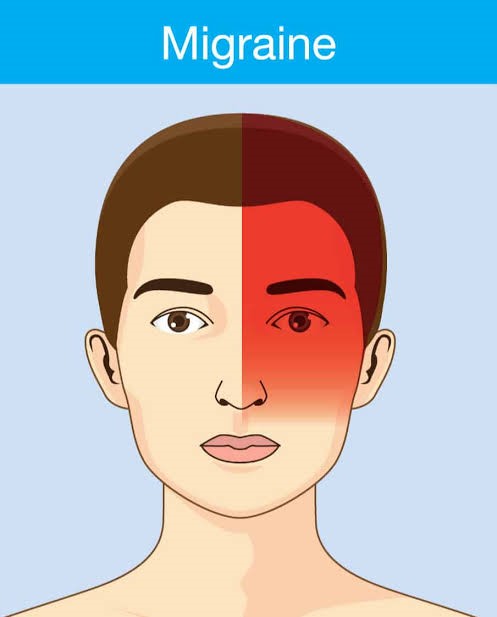
Migraine.
Throbbing migraine headaches usually affect one side of the head only (in some cases on both sides, all over the head, or back of the head). It is episodic in nature and may last a few hours or a few days. It may be preceded by or accompanied by an aura or warning consisting of unusual visual symptoms in the form of wiggly lines /dark or white spots. It is usually accompanied by nausea or vomiting, increased sensitivity of light or noise. There may be a family history of migraine. Certain food items or drinks sometimes provoke migraine attacks. Surprisingly migraine is more common in women than in men.
Cluster Headache.
Cluster head ache is characterized by sharp pain that usually affects one side of the head and is felt in or around the eye or forehead. It is usually accompanied by nasal congestion and redness or watering of the eye on the same side as the headache. The eye lid may droop and pupil may be constricted. It affects males much more than females, who rarely suffer from it.
Chronic Daily Headache. As the name indicates, this head ache is of monotonous regularity –it occurs daily or almost daily. Four basic types of head ache qualify as “chronic daily headache”. These are chronic tension type headaches, so called transformed migraine, new daily persistent headache, and the condition medically known as hemicranias continua.
Tension Headache.
The pain caused by tension headache is described as pressure or heaviness around the head or top of the head sometimes accompanied by a feeling of soreness or tightness in the back of the neck and shoulders. Sufferers feel as if there is a rubber band around the head sometimes accompanied by a feeling of soreness or tightness in back of the neck and shoulders. Sufferers feel as if there is a rubber band around the head. Other symptoms may include tiredness, lack of energy in concentration, or poor memory. This type of headache lasts for more than four hours, and most patients describe it as being constantly present.
Sinus Headache. This a dull throbbing pain affecting the region around the eyes too. it is usually linked to allergies, sinus infection, and changes in the weather.
Rebound Headaches. These headaches are characterized by a continuous low grade head ache between several episodes of increased pain throughout the day. Such headaches are a result of the wearing off of the effects of the pain killer. These headaches may be triggered by slight physical or mental effort. These are often accompanied by nausea, restlessness, anxiety, irritability, memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and depression.
Ice-cream Headache. Medically called cold stimulus headache, this is sometimes caused by gulping down a frozen dessert (say an ice cream), which triggers an excruciating, sharp, shooting
pain. This is caused by blood vessel spasms which are triggered by the intense cold. To avoid this, just go slow while eating your ice cream.
Migraine is one of the most common headache for which Electrohomeopathy can positively do something. Here, there is another special significance. In allopathic medicine, there is no remedy for this disease. So it is common to find patients coming for Electrohomeopathy treatment after suffering for 10 to 15 years, despite allopathic treatment.
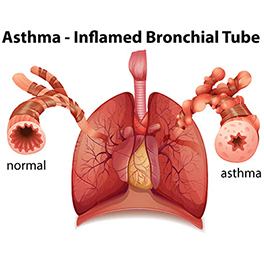
Asthma is chronic inflammatory disease of the airways caused by a verity of triggering factors, which causes recurrent episodes of dyspnoea, chest tightness and wheezing. It is also at times referred to as "Bronchial Asthma" as the main involvement is of the bronchi.
1)The tendency to develop asthma is hereditary and patients have at least one other affected family member suffering from asthma or skin disease like eczema. 2)Asthma is often a part of atopic syndrome. Atopy is an inherited allergic hypersensitivity affecting parts of body and involves eczema, allergic conjunctivitis, allergic rhinitis and asthma.
1)Inhalant allergens like pollen grains, house dust mites, mold spores, animal dander etc.
Irritants like tobacco smoke, air pollution, dust, volatile organic compounds, including perfumes, soap, detergents, air fresheners etc.
2)Repeated URTI infections, especially viral respiratory infections can trigger asthma with chronicity.
3)Occupational asthma may occur due to constant exposure to chemicals gases, metals, animal products, wood dust, plastic resin, and biological enzymes in work place.
4)Cold and rainy weather or extreme changes in temperature can make it harder for asthmatics to breathe.
5)Medications including Aspirin, beta blockers are known to cause bronchospasam in susceptible individual.
6)Gastroesophagal reflux has been has been recognized as a common trigger of asthma.
7)Emotions like laughter, tension, stress, anxiety, and even exercise may trigger an attack of asthma in weak individuals.
8)Hormonal changes in adolescent girls & adult women during their menses and sometimes pregnancy can lead to worsening of asthma.
Childhood onset asthma or Allergic asthma Adult onset asthma or Intrinsic asthma
The three main cardinal symptoms of asthma are:
1)Wheezing - a whistling or hissing sound when breathing out.
2)Shortness of breath - especially with exertion or at night & may occur after exercise or when exposes to cold, dry air.
3)Coughing - may be chronic, usually worse at night & early morning & may occur after exercise or when exposed to cold, dry air.
Treatment of a Electrohomeopathy from Qualified and Experienced Electrohomeopathy Doctor on time, can save patient from dependency on inhalers/bronchodilators, antibiotics, anti-histamines etc & also improve their overall immunity towards such respiratory ailments.
After detail case taking a Electrohomeopathy will give you a constitutional medicine which will reduce the recurrences of attacks. This will help to lead the treatment towards cure in short span of period.
Self medication is not advisable.
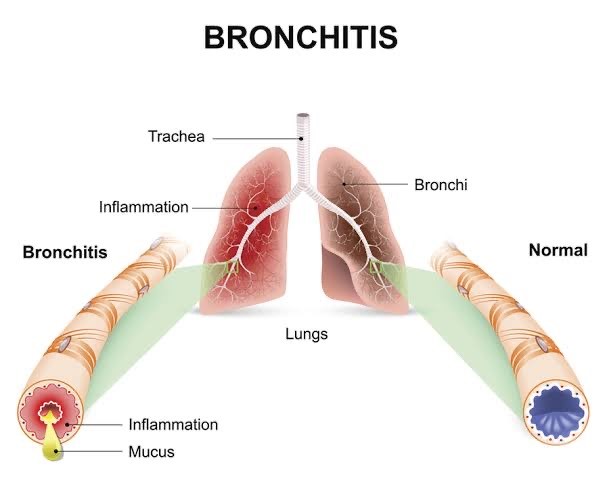
Bronchitis is a lower respiratory tract infection which results due to bronchial tube inflammation.
1)Acute Bronchitis Acute bronchitis occurs most frequently during the winter lasting for few days or weeks. Acute bronchitis is mostly self-limiting, that is, the body`s defense clears the infection. But prompt treatment is advisable to prevent complications like bronchopneumonia.
It often follows an upper respiratory tract infection, such as a cold or flu and may accompany a bacterial infection.
It may also occur when acids from the stomach consistently back up into the food pipe, a condition known as gastroesophagial reflux disease (GERD) leading to irritation of the passage.
Workers exposed to certain dusts or fumes may develop occupational bronchitis.
Chronic Bronchitis is not necessarily caused by infection and is generally part of a syndrome called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Affected individual has persistent cough that produces sputum & mucus, for at least three months in two consecutive years.
Cigarette smoke, including long term exposure to second-hand smoke, is the main cause of chronic bronchitis
A series of attacks of acute bronchitis
Treatment of a Electrohomeopathy from Qualified and experienced Electrohomeopathy Practitioner, on time, can save patient from dependency on inhalers / bronchodilators, antibiotics, anti-histamines etc & also improve their overall immunity towards such respiratory ailments.
For chronic & acute conditions patient needs constitutional treatment to reduce the recurrence and to build resistance & immunity which will lead the treatment towards cure in short span of period.

Cough is a symptom that has been experienced by almost every individual from time to time. It is a protective, primitive reflex whose action secures the removal of mucus, noxious substances & infections from the larynx, trachea & larger bronchi.
1)Acute - Lasting less than 3 weeks
2)Chronic - Lasting more than 8 weeks
3)Productive Cough - Cough with phlegm or 4)mucus(sputum)
5)Non-productive cough - Cough is dry and does not produce phlegm or mucus(sputum)
1)Infections - An infection of the lungs or upper airway passage due to common cold (most frequently), pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis, etc.
2)Postnasal drip syndrome - Excessive mucus accumulated in the back of nose drains down into the throat & excites cough. Can be caused by rhinitis or sinusitis.
3)Chronic lung diseases - It can be a sign of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease such as bronchitis.
4)Factors leading to Non-productive cough (without phlegm) include:
5)Bronchospasm - Irritation may lead to spasm of the bronchial tubes with dry cough, more commonly at night or early morning.
6)Allergies - Allergic rhinitis, etc
7)Occupational factors - Exposure to dust, fumes and chemical in the work environment.
8)Smoking - Cigarette smoking or exposure to passive smoke.
9)Foreign body in airways - Airway obstruction due to an inhaled object such as food,, a piece of balloon or a small toy.
10)Croup - A viral inflammation of larynx, windpipe and bronchial passage that produces the bark like cough in infants and in young children between 3 months & 3 years.
11)Bronchiolitis (inflammation of bronchioles, the smallest air passages of lungs) - most commonly affecting infants with recurrent cough wheezing & breathlessness.
12)Asthma - A chronic dry cough may be a sign of mild asthma with wheezing, shortness of breath or a feeling of tightness in the chest.
Consult a Qualified and experienced Electrohomeopathy Doctor for the appropriate treatment. For chronic & acute conditions patient needs constitutional treatment to reduce the recurrence of attacks and to build resistance & immunity which will lead the treatment towards cure in short span of period. Self medication is not advisable.
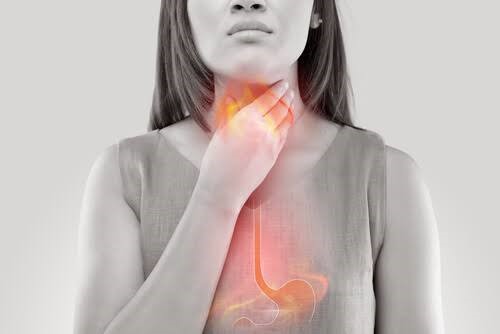
Almost everyone has acidity or heartburn sometimes. Heartburn is a substurnal (behind the chest bone) pain It is a pain or burning sensation , usually associated with a reflux of gastric juices into the esophagus. The pain often rises in the chest and throat.
The cause of acidity might be pregnancy, certain foods, alcohol and some allopathic medications. Treating acidity is important because over time reflux can damage the esophagus.
A cup full of cold milk without sugar taken during the attack, gives immediate but temporary relief.
1)Don't lie down soon after eating.
2)Lose weight, if you are overweight.
3)Do not smoke or cut down it.
4)Avoid fatty & spicy food, alcohol & foods containing caffein
Consult a Qualified Electrohomeopathy Physician for the appropriate treatment. For chronic & acute conditions patient needs constitutional treatment to reduce the recurrence and to build resistance & immunity which will lead the treatment towards cure in short span of period.
Most people ignore their digestive system unless there’s a problem. They rarely consider the role it plays in our overall health. People with poor digestive health might struggle with their weight, experience irregularity, nausea, bloating, constipation, stomach pain, diarrhoea, heartburn, or gas on a routine basis. Poor digestive health also can prevent people from sleeping, working, exercising, or socializing with friends.
Your digestive system is continuously at work throughout the day, helping to nourish your body and mind. Digestive disorders encompass a wide array of conditions that affect the gastrointestinal tract. These disorders vary in severity, from minor annoyance (such as mild heartburn) to potentially life-threatening illness (such as a perforated ulcer).
The digestive system is an intricate system that can be disrupted by disease, diet, and emotional stress. Common digestive problems such as heartburn/GERD, IBD, and IBS cause millions of people to suffer daily and limit quality of life. Digestive problems often result in symptoms such as bloating, diarrhoea, gas, stomach pain, and stomach cramps.
To understand why digestion is so important, you must first understand the digestive process that occurs in your body. When you digest food, it is broken down into nutrients, which feed your body and keep it working well. Your body is made up of billions of cells. Like tiny building blocks, they work together to form every part of you. Cells make up your skin, bones, muscles, and organs. Your body uses nutrients to fix damaged cells and make new ones. Nutrients give cells what they need to work, grow, and divide.
Digestion begins in the mouth, where food and liquids are taken in, and is completed in the small intestine. The digestive system supports the human body. It is composed of a series of organs that break down and absorb the food you eat so that the nutrients can be transported into the blood stream and delivered to cells throughout the body.
Your skin, hair, and even sleep can be affected by poor digestive system. If you have good digestive health, you should be close to a normal weight and go days without experiencing symptoms like heartburn, gas, constipation, diarrhoea, nausea, or stomach pain.
Digestive symptoms include a wide variety of symptoms that affect the digestive or gastrointestinal system. The gastrointestinal system includes the throat, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. Digestive symptoms can be due to a wide variety of mild to serious diseases, disorders and conditions. They can occur in all age groups and populations.
1)Abdominal pain
2)Abdominal swelling, bloating or distension
3)Belching
4)Burning in the throat
5)Constipation
6)Diarrhoea
7)Gas and flatulence
8)Indigestion
9)Nausea
10)Reflux
11)Vomiting
Digestive symptoms may be accompanied by symptoms in other body systems depending on the underlying disease, disorder or condition. Other symptoms that may occur along with digestive symptoms include:
1)Chest pain or pressure
2)Chills
3)Dizziness
4)Easy bleeding or bruising
5)Flu-like symptoms (fatigue, fever, sore throat, headache, cough, aches and pains)
6)Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
7)Pale skin
8)Referred shoulder pain
9)Weakness (loss of strength)
10)Weight loss, mal absorption, and vitamin deficiencies.
Electrohomeopathy is a safe and useful way to treat various digestive disorders, including indigestion, stomach aches, bloating, gas, ulcers, constipation, diarrhoea, acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome, heartburn, and Crohn’s disease.
When someone has a stomach-ache, the body is signalling that something is not right within the patient. By using a painkiller, the patient masks the pain and does not treat the underlying imbalance. This can lead to other, worse conditions for the patient. Electrohomeopathy remedies do not mask symptoms. Rather, they hone in on the underlying cause of problem.
Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Nearly everyone becomes constipated at one time or another. Usually, this condition is not serious. Older people are five times more likely to complain about the symptom than younger people, possibly because of an undue concern about their bowel movement. To avoid most of the problems related to constipation, it helps to know what causes it, how to prevent it, and how to treat it. Experts agree that older people often worry too much about having a bowel movement every day. Normal frequency of bowel movement or volume of stool varies widely from person to person. A decrease in the frequency of bowel movements, accompanied by prolonged or difficult passage of stools, or a sense of incomplete evacuation are all expressed constipation. Constipation is a common symptom among older people.
Older adults are more likely to have constipation for the following reasons:
1)Poor diet Eating foods rich in animal fats (dairy products, meats, and eggs) or refined sugar but low in fibre (whole grains, fruits, and vegetables).
2)Inadequate fluid intake: Not drinking enough water can lead to hard dry stools. Fluid is absorbed in the intestine, and people who don’t drink enough water may not pass enough water into the colon to keep their stools soft.
3)Caffeine and alcohol: These induce increased urination of water. This leads to (relative) dehydration that increases water absorption from the intestine. This can in turn lead to constipation when not enough fluid is retained in the stool.
4)Poor bowel habits: Ignoring the desire to have bowel movements may initiate a cycle of constipation. After a period of time, the person may stop feeling the desire to move the bowels. This leads to progressive constipation. For example, some people may avoid using public toilets or ignore going to the toilet because they are busy.
5)Medications: Many medications can cause constipation like Antacids, Antispasmodic drugs, Antidepressants, Iron tablets, Anticonvulsant drugs, Diuretics (because they can work like caffeine and alcohol as mentioned previously), Painkillers, narcotic-containing drugs, for example, may suppress bowel function.
6)Lack of exercise. Prolonged bed rest, for example after an accident or during an illness.
7)Habitual use of enemas and laxatives - The person may eventually require increasing amounts of laxatives to move the bowels. In some instances, the bowel will become insensitive to laxatives and the person will not be able to move the bowels even with laxatives.
8)Travel: Changes in lifestyle, low fluid intake, and eating fast food may cause constipation.
9)Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Because of changes in bowel function, if a person has this disorder, he or she may have crampy abdominal pain, excessive gas, bloating, and constipation, sometimes alternating with diarrhoea.
10)Connective tissue diseases: Conditions such as scleroderma and lupus.
Symptoms of constipation depending on his or her normal bowel habits, diet, and age.
Symptoms include:
1)Difficulty in starting or completing bowel movement
2)Infrequent and difficult passage of stool, Passing hard stool after prolonged straining
3)If the person has irritable bowel syndrome(IBS) then crampy abdominal pain, excessive gas, a sense of bloating, and a change in bowel habits
4)If the person has an intestinal obstruction, nausea, vomiting, no defecation, and inability to pass gas, Distended abdomen, headaches, and loss of appetite
5)Coated (furred) tongue, bad breath(halitosis), and bad taste in the mouth
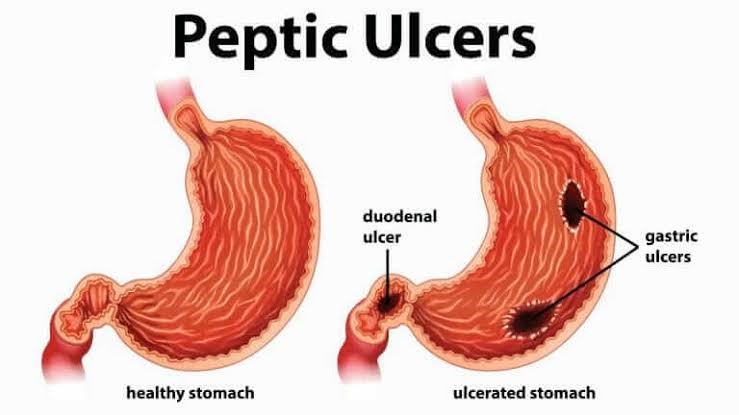
Peptic or Duodenal ulcers are lesions (holes or breaks) in the lining membrane of the stomach or duodenum. It occurs at the lower end of esophagus, in the stomach or in the duodenum which is the first part of small intestine.
A burning stomach pain is the most common symptom of ulceration. The pain is often on and off.
The Pain may come and go for a few days or weeks. It might bother you more when your stomach is empty Usually goes away after you eat.
Then again after eating you feel all gone sensation.
Peptic ulcers happen when the acids that help you digest food damage the walls of the stomach or duodenum. Peptic ulcers will get worse if not treated.
The most common cause is infection with a bacterium, long-term use of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin .Stress and spicy foods do not cause ulcers, but it can make them worse.
This patient needs strict advice about the diet and food habits. Patient should take his food in regular intervals.
Highly seasoned food and stimulants should avoid. Avoiding smoking and alcohol also helps.
Prevention for Ulcers
1)Below are some hints for changes in lifestyle for avoiding esophageal and other gastric ulcers and acidity.
2)leep with your head 6" above your bed.
Do not eat or drink foods with caffeine or alcohol.
3)Avoid citrus juices, tomatoes and hot spicy food.
4)Eat small meals at shorter intervals about six times each a day.
5)Do not eat immediately before going to bed.
Electrohomeopathy offers freedom from ulcers. Conventional treatment gives only temporary symptom relief. So more often than not, ulcers keeps returning. As the problem becomes chronic, conventional treatment gets less effective. In such chronic cases patient gets benefit from Electrohomeopathy constitutional treatment. Therefore more and more people are turning towards Electrohomeopathy for relief from this troublesome disease.
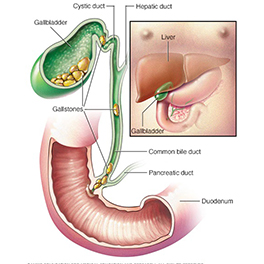
The gallbladder is a small little pouch that is shaped like a pear, and it is located behind the liver. Its primary duty is to save the cholesterol-rich bile that’s secreted from the liver. Bile helps the body digest fatty foods.
Therefore, when that bit of fatty steak reaches the intestines, they deliver a note to send down some bile from the gallbladder. After this the fatty food becomes easier to digest and readily makes its way through the remainder of the digestive procedure.
Gallstones (also known as cholelithiasis) are pieces of solid material that form in the gallbladder. These stones develop because cholesterol and pigments in bile sometimes form hard particles. Gallstones usually form in the gallbladder; however, they also may form anywhere there is bile; in the intrahepatic, hepatic, common bile, and cystic ducts. A gallstone is a crystalline concretion formed within the gallbladder by accretion of bile components. These calculi are formed in the gallbladder but may distally pass into other parts of the biliary tract such as the cystic duct, common bile duct, pancreatic duct, or the ampulla of Vater.
On the basis of their composition, gallstones can be divided into the following types:
Cholesterol stones vary from light yellow to dark green or brown and are oval, between 2 and 3 cm long, each often having a tiny, dark, central spot. To be classified as such, they must be at least 80% cholesterol by weight (or 70%, according to the Japanese- classification system).
Pigment stones are small and dark and comprise bilirubin and calcium salts that are found in bile. They contain less than 20% of cholesterol (or 30%, according to the Japanese classification system).
Mixed gallstones typically contain 20–80% cholesterol (or 30– 70%, according to the Japanese classification system). Other common constituents are calcium carbonate, palmitate phosphate, bilirubin, and other bile pigments. Because of their calcium content, they are often radio graphically visible.
Causes of Gallstones
Gallstone risk increases for females (especially before menopause) and for people near or above 40 years. Several factors may come together to create gallstones, including: Genetics, Body weight, Decreased motility (movement) of the gallbladder, Diet.
Gallstones can form when there is an imbalance in the substances that make up bile. For instance, cholesterol stones may develop as a result of too much cholesterol in the bile. Another cause may be the inability of the gallbladder to empty properly.
Pigment stones are more common in people with certain medical conditions, such as cirrhosis (a liver disease in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue) or blood diseases such as sickle cell anemia.
Genetics. If other people in your family have had gallstones, you are at increased risk of developing gallstones.
Obesity. This is one of the biggest risk factors. Obesity can cause a rise in cholesterol and can also keep the gallbladder from emptying completely.
Estrogen. Estrogen can increase cholesterol and reduce gallbladder motility. Women who are pregnant or who take birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy have higher levels of estrogen and may be more likely to develop gallstones.
Gender and age. Gallstones are more common among women and older people.
Cholesterol drugs. Some cholesterol-lowering drugs increase the amount of cholesterol in bile, which may increase the chances of developing cholesterol stones.
Diabetes. People with diabetes tend to have higher levels of triglycerides (a type of blood fat), which is a risk factor for gallstones.
Rapid weight loss. If a person loses weight too quickly, his or her liver secretes extra cholesterol, which may lead to gallstones. Also, fasting may cause the gallbladder to contract less.
The role of diet in the formation of gallstones is not clear. We do know that anything that increases the level of cholesterol in the blood increases the risk of gallstones. It is reasonable to assume that a diet with large amounts of cholesterol and other fats increases the risk of gallstones, but it is also important to remember that the amount of cholesterol in our bile has no relationship to our blood cholesterol. Losing weight rapidly seems to increase the risk of gallstones and so does skipping meals. Obesity is a risk factor for gallstones. Eating a fatty or greasy meal can precipitate the symptoms of gallstones.
Most people with gallstones have no symptoms called “silent gallstones”. In fact, they are usually unaware that they have gallstones unless symptoms occur.
Symptoms usually occur as complications develop. The most common symptom is pain in the right upper part of the abdomen. Because the pain comes in episodes, it is often referred to as an “attack.”
Attacks may occur every few days, weeks, or months; they may even be separated by years.
ease by dissolving the stone through proper remedies. With Electrohomeopathy treatment one can successfully control the pain as well as the swelling of gall bladder. It also arrests further development of the gall bladder stones. To avoid recurrence of gall stone Constitutional line of treatment must be given.
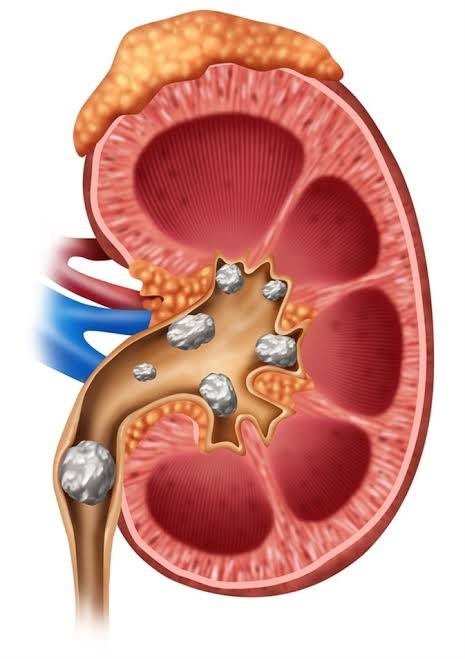
There are various causes behind the formation of kidney or renal stones of which dietary factor plays a vital role. Lifestyle changes, changing trends in food habits, low fluid intake, etc. increase the risk of developing renal stones.
Certain other factors like physiological changes in the urine (eg. urinary pH, specific gravity, etc.), urinary tract infection, urinary stasis, hyperexcretion of urinary constituents such as oxalates, calcium, uric acid, cystine and conditions like hyperparathyroidism, hyperoxaluria, etc. are favourable conditions in the urinary system for the formation of urinary stones by a situation of super-saturation due to failure of in-built mechanism to prevent it.
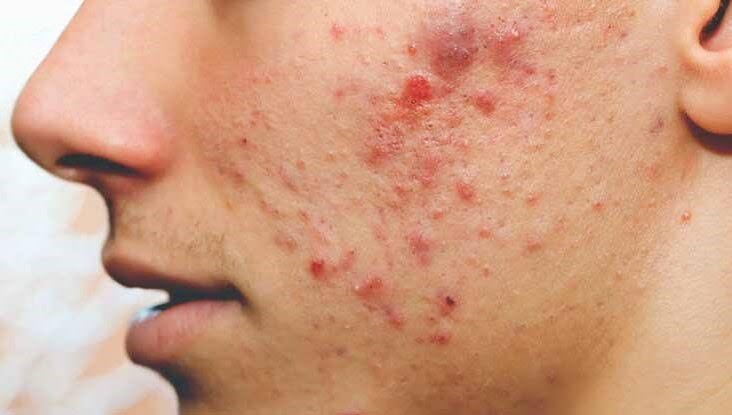
Acne or Pimples is an inflammatory disease of sebaceous (oil) glands. it is nothing but development of small eruptions on face neck, back, chest and shoulders. During puberty and pregnancy, sex hormones speed up the secretion of oil from glands. Problem begins where there is build up of oil in the narrow gland openings or drainage passages in the skin. It is therefore, important, that the perspiration and other coatings clogging the skin pores be washed off. Acne should not be squeezed as it leads to inflammation and scaring. Stress doesn't cause acne, but it can make pimples worse. Blackheads and pimples are not caused by dirt.
White heads: Round white blemishes the form when hair follicles became clogged. Black heads: Round dark blemishes that form where white heads reach the skin's surface and touch air. Pimples: Red swollen bumps that form when plugged follicle walls breaks near the skin's surface. Deep cysts: Pimples filled with pus that forms when plugged follicle walls break deep within the skin.
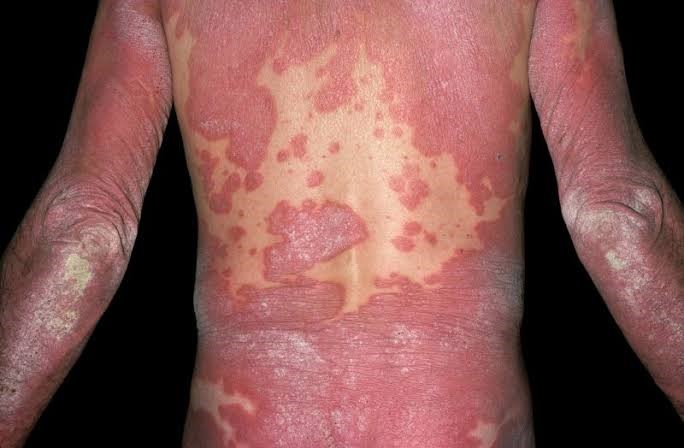
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease that affects the skin. It is typically a lifelong condition Psoriasis occurs when the immune system mistakes a normal skin cell for a pathogen, and sends out faulty signals that cause overproduction of new skin cells. It is not contagious. Psoriasis has been linked to an increased risk of stroke, and treating high blood lipid levels may lead to improvement.
There are five types of psoriasis: plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic. Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin condition. The obvious sign is the colour change associated with the plaques (the raised patches in the skin), although this is more obvious where there is little scale. In fair skinned people, the plaque will look red (sometimes referred to as salmon pink), whereas in dark-skinned individuals the plaque tends to look a darker shade of the normal skin. Often, however, the white scaling is thick and hides the redness, so psoriasis looks thick, white and, crusty on exposed surfaces regardless of the underlying skin colour. The thickening is caused by the greatly increased ‘turnover’ of the skin cells. Normally, a living skin cell moves upward from the bottom layer of skin, loses its nucleus and dies. It is then largely made up of a protein called keratin and is shed from the surface of the skin as new cells go through the same process and replace it from underneath. The whole process takes around 28 days, but in psoriasis it is greatly speeded up to 3-4 day cycle. Living cells are then much closer to the surface, and as they still need a blood supply, the vessels lie closer to the surface, leading to the redness and heat that many people with psoriasis complain of. The fact that the surface cells are being replaced before they are shed results in a thick layer of scale, which, as everyone with the condition knows, flakes off readily and abundantly.
The cause of psoriasis is not fully understood. There are two main hypotheses about the process that occurs in the development of the disease. The first considers psoriasis as primarily a disorder of excessive growth and reproduction of skin cells. The problem is simply seen as a fault of the epidermis and its keratinocytes. The second hypothesis sees the disease as being an immune-mediated disorder in which the excessive reproduction of skin cells is secondary to factors produced by the immune system.
Genetic predisposition: A positive family history may predispose you to be affected by this condition. General Aggravating Factors These are responsible for aggravating or causing the lesions to reappear: Physical & Emotional Stress Seasonal chanPepges: Winter months may cause an increase in dryness and may aggravate psoriasis Environmental factors - Skin irritants, local trauma, infections, alcohol, steroid withdrawal etc.
Sites of predilection, Include scalp, retro auricular area, knees, elbows, sacrum, and nails, Lesion morphology– sharply bordered erythematous patches and plaques with silvery scale. Psoriasis is often diagnosed by a dermatological or primary care physician by its,characteristic appearance and locations on the body. If a person has the skin changes typical of psoriasis, a diagnosis can be made clinically by examination alone, based on the skin's appearance due to psoriasis, a physician will usually be able to diagnose psoriasis and being treating the skin immediately. If person looks different than most cases, appears in an unusual location, further test may be needed. The definitive test when a clinical diagnosis of skin disease is a skin biopsy. Usually one test is required, but it may be repeated if the results are not clear or the disease changes over time. No blood test exists to diagnose psoriasis, and psoriasis does not cause abnormal blood tests for most people.
Psoriasis is a condition capable of affecting one’s career, relationships and confidence. Patients have been treated for years with conventional medicine resulting in only remission of the symptoms for a while, leading to a flare-up again. Psoriasis is a chronic condition which needs to be treated holistically, from the inside. Electrohomeopathy has shown significant success with Psoriasis patients.In Psoriasis, our immunity needs to be strengthened from within and should be able to identify all our body cells as its own
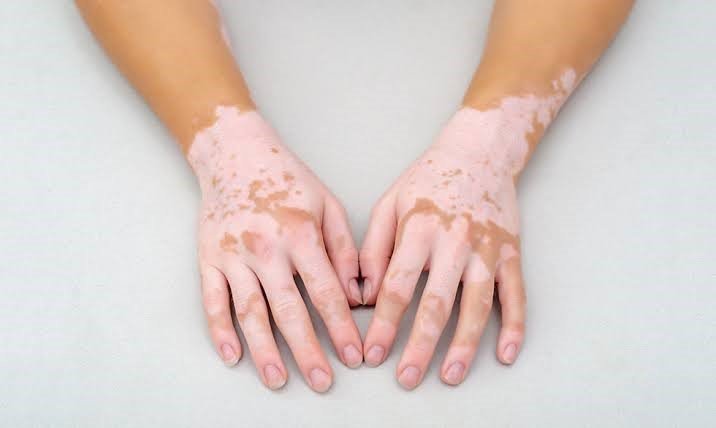

Vitiligo is a condition that causes depigmentation of sections of skin. It occurs when melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation, die or are unable to function. Homoeopathy is able to give wonderful and miraculous cures in many cases of vitiligo. This is due to the fact that homoeopathic treatment enhances the natural production of pigments. According to homoeopathic philosophy, vitiligo is not a disease in itself but an expression of an inner disturbed state of the body. Vitiligo is a condition that causes depigmentation of sections of skin. It occurs when melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation, die or are unable to function. In the case of vitiligo, we believe that the immune system probably sees the person’s own pigment cells as foreign bodies, and attacks them, destroying them or weakening them. There is increasing evidence to support the view that vitiligo is an autoimmune disease and that it shows a familial trait in about 18% of cases. Vitiligo is a benign skin disorder due to loss of pigment. Estimated 1.2% of American and world population, about 8% of Indian and Mexican population suffer with this disorder.
Vitiligo is more common in people with certain autoimmune diseases (diseases in which a person’s immune system reacts against the body’s own organs or tissues). Autoimmune diseases that are associated with vitiligo include: hyperthyroidism (overactivity of the thyroid gland), adrenocortical insufficiency (the adrenal gland does not produce enough of the hormone corticosteroid), alopecia areata (patches of baldness), and pernicious anemia (a low level of red blood cells caused by the failure of the body to absorb vitamin B12). The basis for the association between vitiligo and these autoimmune diseases is not well understood. Moreover, the connection between them seems optional. Most people with vitiligo, fortunately, have no autoimmune disease such as hyperthyroidism, adrenocortical insufficiency, alopecia areata or pernicious anemia.
The cause of vitiligo is not fully known, but there are several theories. One theory of some substance is that people with vitiligo develop antibodies that, instead of protecting them, turn upon them and destroy their own melanocytes, the special cells that produce the pigment melanin that colors their skin. Another theory is that the melanocytes somehow attack and destroy themselves. Finally, some people with vitiligo have reported that a single event such as a severe sunburn or an episode of emotional distress seem to have triggered their vitiligo. Events of this nature, however, have not been scientifically proven to cause vitiligo and may simply be coincidences. Vitiligo may be hereditary and run in families. Children whose parents have the disorder are more likely to develop vitiligo. However, most children will not get vitiligo even if a parent has it, and most people with vitiligo do not have a family history of the disorder.
An important aspect of vitiligo is the psychological effect of the disease. Vitiligo is often immediately visible to others and those with the condition may suffer social and emotional consequences including low self-esteem, social anxiety, depression, stigmatization and, in extreme cases, rejection by those around them. In people with a pale white skin colour, vitiligo may cause little concern.
People with Vitiligo develop white patches on their skin of irregular shapes and sizes. Vitiligo is more common on the exposed areas for example hands face, neck and arms. It also occurs on covered areas too: – like genitals, breast and legs. In some patients the hair may also turn grey early and in the inside of the mouth, white discoloration may also occur. The spread of Vitiligo cannot be determined. It may stop completely after the first patch but often these patches do spread. For some patients further development may takes years and for others the large areas can be covered in months. In some patients mental stress has been seen to increase the growth of these white patches. The three main diseases that can be mistaken for vitiligo are tinea (pityriasis) versicolor, piebaldism and guttate hypomelanosis.
Vitiligo is also known as leucoderma , which is technically not correct. Leucoderma simply means white (leuco) skin (derma), i.e. a disorder where the skin loses its normal color. Leukoderma is a cutaneous condition, an acquired condition with localized loss of pigmentation of the skin that may occur after any number of inflammatory skin conditions, burns, intralesional steroid injections, postdermabrasion, etc In case of leucoderma, there is partial and superficial pigment loss; while in case of vitiligo there is deep and complete pigment loss.
Foods that are excessively sour should be avoided. The ascorbic acid in sour foods tends to reduce melanin pigmentation. So the patients should restrict their intake of citrus foods. Non vegetarian foods are also to be avoided as they act as a foreign body to pigment cells. Flavoured drinks are to be avoided. Artificial colours used in various food preparations should also be avoided. There may not be enough scientific evidence to prove how these foods worsen vitiligo.
Electrohomeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that Electrohomeopathy treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. Electrohomeopathy is able to give wonderful and miraculous cures in many cases of Vitiligo. This is due to the fact that Electrohomeopathy treatment enhances the natural production of pigments. Thus, the cure should occur at a level where things have gone wrong.

Menopause, or the permanent end of menstruation and fertility, is a natural biological process, not a medical illness. Even though, the physical and emotional symptoms of menopause can disrupt your sleep, sap your energy and trigger feelings of sadness and loss.
Hormonal changes cause the physical symptoms of menopause, but mistaken beliefs about the menopausal transition are partly to blame for the emotional ones. First, menopause doesn't mean the end is near - you've still got as much as half your life to go. Second, menopause will not snuff out your femininity and sexuality. In fact, you may be one of the many women who find it liberating to stop worrying about pregnancy and periods.
Menopause occurs anywhere between 35 to 55 years of life. Menopause before age 35 may occur as a result of a surgical procedure, treatment of a disease, or illness. In these cases it is referred to as induced or premature Menopause. Each woman experiences menopause differently. Menopause is an important time in a woman's life. Her body is going through changes that can have an effect on her social life, her feelings about herself, and her performance at work. Contrary to the old-fashioned view that life is all downhill after menopause, many women today find that the years after menopause offer new recognition and fresh beginnings. To have a positive attitude towards menopause as a natural, essential and healthy phase of womanhood is important.
Technically, you don't actually "hit" menopause until it's been one year since your final menstrual period. The symptoms of menopause, however, often appear long before the one-year anniversary of your final period. They include: Irregular periods Decreased fertility Vaginal dryness Hot flashes Sleep disturbances Mood swings Increased abdominal fat Thinning hair Loss of breast fullness
Menopause begins naturally when your ovaries start making less estrogen and progesterone, the hormones that regulate menstruation. The process gets under way in your late 30s. By that time, fewer potential eggs are ripening in your ovaries each month, and ovulation is less predictable. Also, the post-ovulation surge in progesterone - the hormone that prepares your body for pregnancy - becomes less dramatic. Your fertility declines, perhaps partially due to these hormonal effects.
These changes are more pronounced in your 40s, as are changes in your menstrual pattern. Your periods may become longer or shorter, heavier or lighter, and more or less frequent. Eventually, your ovaries shut down and you have no more periods. It's possible, but very unusual, to menstruate every month right up to your last period. You're much more likely, though, to have a gradual tapering off.
Unfortunately, there's no way to know exactly which period will be your last. You have to wait until well after the fact - 12 months after, by official definition. In your final months before reaching menopause, it's still possible to get pregnant, but it's quite unlikely.
Because this process takes place over years, menopause is commonly divided in to the following two stages:
Perimenopause - This is the time you begin experiencing menopausal symptoms, even though you still menstruate. Your hormone levels rise and fall unevenly, and you may have hot flashes and other symptoms. Perimenopause may last four to five years or longer.
Post menopause - Once 12 months have passed since your last period, you've reached menopause. Your ovaries produce much less estrogens and no progesterone, and they don't release eggs. The years that follow are called post menopause.
Electrohomeopathy is the safest treatment before, during, and after menopause because it stimulates the natural hormonal balance without the use of harmful drugs. Constitutional Electrohomeopathy treatment is best during the transitional period of menopause in order to balance hormonal levels and cure the many accompanying symptoms.
Electrohomeopathy is reassuring and helpful for both physical and emotional aspects of menopause, and most women, in addition to relief from their discomforts, experience an enhancement in self-awareness and well being after the treatment. Thus you can rely on Electrohomeopathy to achieve optimal health during menopause and into the later years of your life. It is of assistance in all sorts of emotional, mental and physical problems that a woman is likely to experience, and can help her through the transitional and developmental milestones of her life.
Fortunately, most of the symptoms associated with menopause are temporary. Note these few steps to help reduce or prevent their effects:
Get regular exercise, dress in layers and try to pinpoint what triggers your hot flashes. For many women, triggers may include hot beverages, spicy foods, alcohol, hot weather and even a warm room.
Use over-the-counter water-based vaginal lubricants or moisturizers. Staying sexually active also helps.
Avoid caffeine and plan to exercise during the day, although not right before bedtime. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, guided imagery and progressive muscle relaxation, can be very helpful. You can find a number of books and tapes on different relaxation exercises. If hot flashes disturb your sleep, you may need to find a way to manage them before you can get adequate rest.
. Pelvic floor muscle exercises, called Kegel exercises, can improve some forms of urinary incontinence. Practicing Yoga will help. Naukasana is beneficial.
Eat a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables and whole grains and that limits saturated fats, oils and sugars. Aim for 1,200 to 1,500 milligrams of calcium and 800 international units of vitamin D a day. Ask your doctor about supplements to help you meet these requirements, if necessary.
Smoking increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, osteoporosis, cancer and a range of other health problems. It may also increase hot flashes and bring on earlier menopause. It's never too late to benefit from stopping smoking.
Get at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity on most days to protect against cardiovascular disease, diabetes, osteoporosis and other conditions associated with aging. More vigorous exercise for longer periods may provide further benefit and is particularly important if you are trying to lose weight. Exercise can also help reduce stress.
Talk with your doctor about how often you should have mammograms, Pap tests, lipid level (cholesterol and triglyceride) testing and other screening tests.
Several young woman today have started to experience the symptoms of hormonal imbalance and of menstrual irregularities beside weight gain, facial hair growth etc. If the symptoms are ignored in the initial stages then they can grow worse as the time passes by. An answer of the common female disorders can help to initiate timely intervention and prevent undue complications. Women's health problems are major yet mostly unattended issues. Being a woman means worrying about a whole bunch of major medical concerns particularly in relation to reproductive system. From missed period to painful periods, menstrual cycle problems are common.
The female reproductive system consists of internal parts i.e. uterus, vagina, ovaries and fallopian tubes and external part i.e. vulva which includes the labia, clitoris and urethra. Woman normally have two ovaries, each about the size of walnut and located on each side of uterus, Ovaries store and release egg.
An ovarian cyst is fluid filled sac surrounded by a very thin wall, within an ovary. Ovarian cyst can affect woman of all ages but common in the reproductive age group. Most ovarian cysts are functional, benign and asymptomatic in nature. However, some may cause problems, such as bleeding and pain.
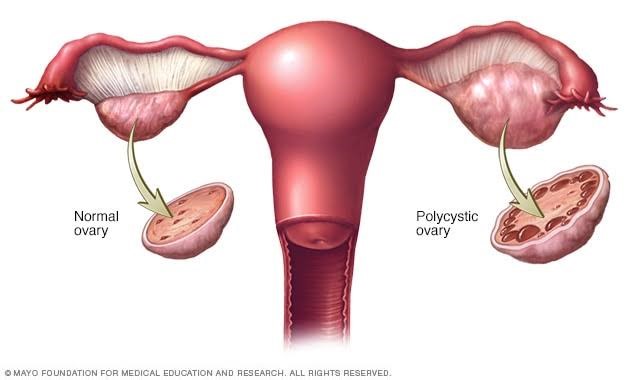
Polycystic-appearing ovary is diagnosed based small cyst present around the outside of the ovary. It can be found in "normal" woman as well as woman with endocrine disorders. Polycystic-appearing ovary is different from the polycystic ovarian syndrome, which includes other symptoms in addition to the presence of ovarian cysts.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by ovaries containing multiple cysts, mild obesity, irregular menses and sign of androgen excess (acne).
In PCOS, the ovaries are bigger than average and the outer surface of ovary has an abnormally large number of small follicles. These follicles remain immature, never growing to full development or ovulating to produce an egg capable of being fertilized. The woman rarely ovulates and so is less fertile. In addition she does not have regular periods and may go for many weeks without periods.
Symptoms typically begin puberty and worsen with time. Some or all the following symptoms may be present, though it is possible not to experience any symptoms.
1 Absent or an infrequent period is a common symptom of PCOS. Period can be as frequent as every five to six weeks, but might only occur once or twice a year, if at all. 2 Increased facial and body hair usually found under the chin, on the upper lip, forearms, lower legs and on the abdomen. 3 Overweight/Obesity A common finding in woman with PCOS because their body cells are resistant to the sugar-control hormone insulin. This insulin resistance prevents cell using sugar in the blood normally and the sugar is stored as fat instead. 4 Acnes Strange nodules that feel like bruises under the layer of skin, oily skin, dandruff and skin discolorations. 5 Infertility Infrequent or absent periods are linked with very occasional ovulation, which significantly reduces the likelihood of conceiving. 6 Miscarriage (sometimes recurrent) one of the hormonal abnormalities in PCOS, a raised level of luteinizing hormone. Woman with raised LH have a higher miscarriage rate compared with those who have normal LH values. 7 Dull Aching Severe, sudden sharp pain or discomfort in lower abdomen. Constant or intermittent pain in pelvis, vagina, thigh & lower back. There may be fullness, heaviness, pressure swelling or blotting or feeling of lump in the lower abdomen. 8 Breast tenderness with pain during or shortly after beginning or end of menstrual period. 9 Change in frequency or ease of urination or difficulty with bowel movements due to pressure on adjacent pelvic anatomy. 10 Non specific symptoms like nausea vomiting, fatigue, headache in some cases.
Electrohomeopathy is very effective in treating women's reproductive problems because it stimulates the body to heal itself rather than inhibit or suppress the bod's attempt to become well. There are Electrohomeopathy remedies that treat women's discomforts related to hormonal changes like premenstrual syndrome, painful periods, PCOS, menstrual irregularities, perimenopause, menopause, recurrent east infections, etc.
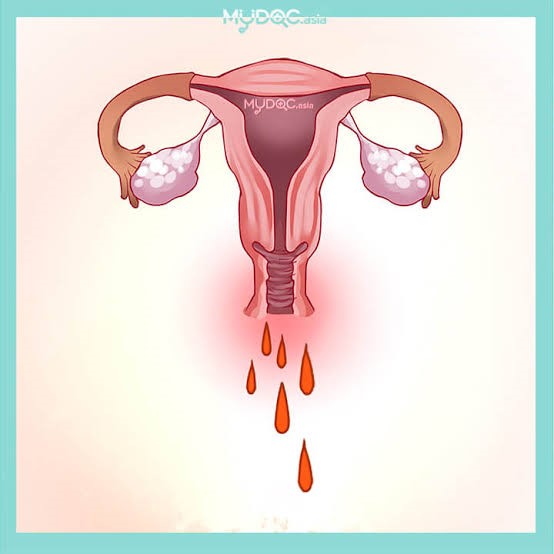
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is a condition that affects nearly every woman at some point in her life, typically in the adolescent or perimenopausal /premenopausal period. It is also called dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB), AUB is a condition that causes vaginal bleeding to occur from uterus outside of the regular menstrual cycle. It is generally occurs due to hormonal disturbances. A normal menstrual cycle is characterized by an approximate flow of 30 mL per period, which lasts for 2 to 7 days and occurs with a mean interval of 21 to 35 days.
Abnormal uterine bleeding can be characterized clinically by amount, duration, and periodicity as
Menstruation occurring with intervals of more than 35 days
menstruation occurring regularly with intervals of less than 21 days
menstrual bleeding occurring at irregular intervals or bleeding between menstrual cycles
regular menstrual cycles with excessive flow (technically more than 80 mL of volume) or menstruation lasting more than 7 days
Menstrual bleeding occurring at irregular intervals with excessive flow or duration.
1)Anovulatory AUB: During an anovulatory cycle, the corpus luteum does not form. Thus, the normal cyclical secretion of progesterone does not occur, and estrogen stimulates the endometrium unopposed. Without progesterone, the endometrium continues to proliferate, eventually outgrowing its blood supply; it then sloughs incompletely and bleeds irregularly, and sometimes profusely or for a long time. When this abnormal process occurs repeatedly, the endometrium can become hyperplastic, sometimes with atypical or cancerous cells.
2)Ovulatory AUB: In ovulatory AUB, progesterone secretion is prolonged; irregular shedding of the endometrium results, probably because estrogen levels remain low, near the threshold for bleeding (as occurs during menses). In obese women, ovulatory AUB can occur if estrogen levels are high, resulting in amenorrhea alternating with irregular or prolonged bleeding. AUB occurs in approximately 10% to 30% of reproductive-aged women and has a negative impact on the quality of life of affected women, whether young or old. Twenty percent of cases of DUB occur in adolescence, and 40% of cases occur in patients over age 40.
Adolescence:
Anovulatory cycles occur in 55% to 82% of female adolescents at menarche and typically continue until 2 years after menarche
Anovulatory bleeding is common among adolescents due to the immaturity of the hypothalamic pituitary- ovarian axis
Perimenopause:
AUB in perimenopausal women is related to declining ovarian function
Observational data show increased variability of the menstrual pattern in women approaching menopause
Obesity:
AUB in overweight women results from altered estrogen to progesterone ratios and increased peripheral conversion of androgens to estrogens. The estrogen-driven endometrial proliferation eventually leads to endometrial overgrowth and abnormal bleeding patterns
Weight loss in obese patients presumably restores regular menstrual cycles by decreasing the adipose tissue available for conversion of androgens to estrogen.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS):
Menstrual irregularity is seen in two thirds of adolescents with PCOS and typically presents with anovulatory symptoms mimicking AUB
Cigarette smoking:
Women who smoke cigarettes have a 47% risk of experiencing abnormal uterine bleeding due to the antiestrogenic effect of cigarette smoke.
Symptoms of dysfunctional uterine bleeding may include:
1)Bleeding or spotting from the vagina between periods.
2)Periods that occur less than 28 days apart (more common) or more than 35 days apart.
3)Time between periods changes each month.
4)Heavier bleeding (such as passing large clots, needing to change protection during the night, soaking through a Sanitary pad or tampon every hour for 2 - 3 hours in a row).
5)Bleeding lasts for more days than normal or for more than 7 days Other symptoms caused by changes in hormone levels may include:
6)Excessive growth of body hair in a male pattern (hirsutism).
7)Hot flashes.
8)Mood swings.
9)Tenderness and dryness of the vagina.
10)A woman may feel tired or have fatigue if she is loses too much blood over time. This is a symptom of anemia.
Electrohomeopathy management for AUB*
Electrohomeopathy plays an effective role in maintaining a normal menstrual cycle in a woman and it effectively cures any period related problems.
Management of AUB primarily involves prescribing a constitutional Electrohomoeopathic remedy capable of working on the uterus and the entire endocrinal system. This approach usually helps in correcting the pathology associated with AUB.
There are numerous Electrohomeopathy remedies capable of influencing this condition. The remedy prescribed is chosen after carefully understanding your entire constitution, which includes:
Presence of any genetic predisposition
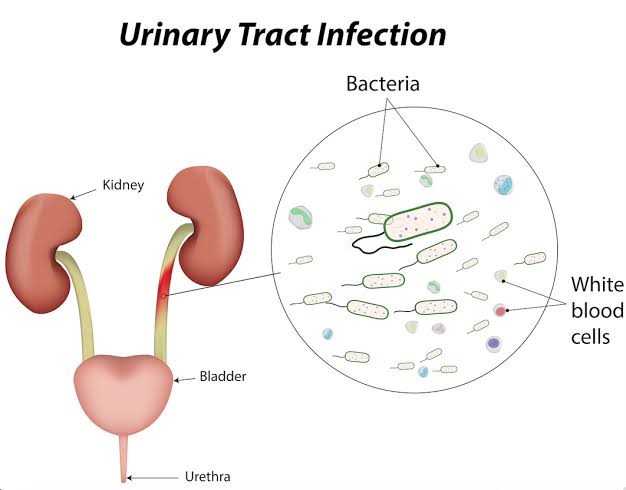
Electrohomeopathy cures stubborn cases of urinary tract infections(UTI) effectively.UTI is an infection that begins in your urinary system. UTI is limited to your bladder can be very painful and annoying. But serious consequences can occur if the infections spread to your kidneys.
Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. Women are most of the risk of developing a UTI. The urinary system is composed of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. All of these components can become infected, but most infections involve the lower tract - the urethra & the bladder.
Urinary tract infection may result in different type of symptoms, depending on which part of your urinary tract is infected: A strong persistent urge to urinate A burning sensation when urinating Passing frequent small amounts of urine Blood in the urine or cloudy strong smelling urine
Electrohomeopathy treatment aims at strengthening the body`s own natural healing powers so that it is able to eliminate the infection itself. Self medication is not advisable.
1)Drink plenty of liquids, especially water.
2)Urinate promptly when the urge rises.
3)Wipe from front to back after urination and bowl movement.
4)Empty your bladder as soon as possible after intercourse.
5)Avoid potentially irritating feminine product like deodorant sprays, powder etc in the genital area.
An Allergy could be described as a sort of modern disease. Allergy has been there earlier also but the incidence of its occurrence is increasing day by day. The word allergy is more abused for various reasons. It is nothing but a condition in which the system over reacts to stimulus. The manifestations depend up to the type of stimulus and the quantum of reaction. There are various types of allergy, and it is humanly not possible to exactly discover the substances that are allergic to an individual. But to a very great extent one can find out the same. Anything in this universe could act as a stimulus (allergen) and cause allergy in an individual. Sometimes it is mental and sometimes it's physical. Simple house dust, metal to a hearty meal could cause allergy.
In conventional treatment allergy is mostly treated by antihistamines & steroids, which generally work for suppressing the symptom. So consult a Qualified Electrohomeopathy Practicener for the appropriate treatment. For chronic & acute conditions patient needs constitutional treatment to reduce the recurrence and to build resistance & immunity which will lead the treatment towards cure in short span of period. According to your disease Electrohomeopathy will give you one of the following remedy to subside your acute phase. Self medication is not advisable.
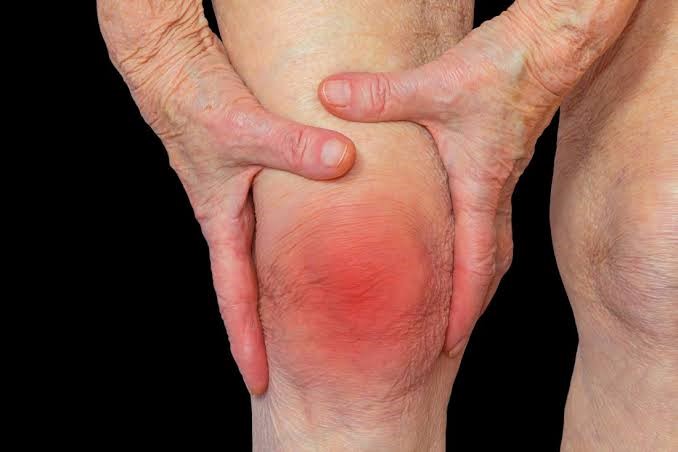
The word arthritis means inflammation of a joint. There are varies verities in this disease. Pain in joints is a common symptom in all types of arthritis. Injuries and venereal diseases also cause arthritis. Any joint may develop inflammatory changes. There will be swelling, redness, pain restricted movements etc. Depending on the type of arthritis, the joints are affected. For example, in Osteo arthritis, bigger joints are affected. In Rheumatoid arthritis smaller joints are affected. Out of all the verities of arthritis, the most dangerous is Rheumatic fever as it always has a tendency to affect the heart.
However, arthritis is always a chronic trouble and at once stage or the other, needs a professional Electrohomeopathy consultation. Consult a Qualified Electrohomeopathy Doctor for the appropriate treatment. Patient also needs constitutional treatment to build resistance & immunity which will lead the treatment towards cure in short span of period. According to your disease Electrohomeopathy will give you one of the following remedy for symptomatic relief.

The liver is the largest organ of the body. It is functionally the most complex organ. It has multiple life-saving functions like metabolism - both anabolic and catabolic. It is responsible for detoxification and eliminates endogenous as well as exogenous (foreign) substances. It takes part in immune reactions, and in the synthesis of coagulation factors. It has exocrine and endocrine functions. As an endocrine organ, it secretes growth factors, angiotensinogen, angiotensin, thrombopoietin, etc. Its exocrine function involves bile production. The liver is a filter and stores different substances (e.g. glycogen, vitamins). It is the site of serum protein (e.g. albumin, prothrombin, fibrinogen) and enzyme synthesis. Metabolic processes (e.g. bilirubin, hormone, carbohydrate, and lipid turnover) and the removal of toxic products are important liver functions. Viral or bacterial infections of liver or infestation with parasites have become common. Diseases of the blood or immune system may also interfere with hepatic metabolism and affect the liver. Many different types of medication (e.g. acetaminophen, tetracycline, oral contraceptives, chlorpromazine, isoniazid, halothane, and androgens) can produce an adverse liver reaction in certain people. Other hepatotoxins (e.g. alcohol, fungal toxins, and anabolic steroids) can cause specific damage to liver cells. Alcohol-induced hepatic injury is a common problem. Toxic hepatitis may be clinically silent or severe enough to lead to the rapid development of hepatic failure. An unhealthy diet may cause liver damage. As a result of these, the liver may exhibit symptoms such as jaundice, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, headache, abdominal pain, dark urine, generalised itching, fever, weight loss, anorexia and depression. Examination findings may include hepatomegaly, abdominal tenderness and liver enzyme abnormalities. The fatty degeneration of the liver is the most common abnormality observed in chronic alcoholics. In patients with underlying cirrhosis, manifestations of portal hypertension may predominate.
1)Jaundice: It is yellowish pigmentation of the skin and mucous membrane, due to increased levels of bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinaemia). It may be due to abnormalities in the formation, transport, metabolism or excretion of bilirubin. It has non-hepatic as well as hepatic causes.
2)Hepatitis (due to Hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D & E): Homoeopathy has a wide scope in viral infections, especially in hepatitis.
3)Alcoholic hepatitis: It is becoming common these days. After heavy drinking, symptoms worsen and tend to vary with the severity and progression of the disease. Sometimes symptoms do not present themselves until the disease is relatively advanced. Common symptoms include abdominal pain and tenderness, ascites, confusion, dry mouth / excessive thirst, fatigue, fever, jaundice, loss of appetite, nausea, weight gain due to ascites, etc.
4)Autoimmune hepatitis: It is inflammation of liver due to immune cells that mistake the liver’s normal cells as harmful invaders. A person with autoimmune hepatitis has autoantibodies circulating in the bloodstream that cause the immune system to attack the liver. The cause is predominantly genetic. However, certain bacteria, viruses, toxins and drugs can trigger an autoimmune response in people who are genetically susceptible to develop an autoimmune disorder.
5)Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Fatty liver, also known as fatty liver disease (FLD), is a reversible condition where large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in liver cells via the process of steatosis (i.e. abnormal retention of lipids within a cell). Some measures like losing weight, regular exercise, improving the diet with fibrous food, avoiding alcohol and fatty substances, controlling cholesterol levels and diabetes are helpful.
6)Cholelithiasis: It is a medical term for gallstone. Aversion to fatty food, abdominal discomfort, nausea and vomiting after meals may be symptoms of cholelithiasis.
7)Bile duct obstruction: It is due to various causes like cysts of the common bile duct, enlarged lymph nodes in the porta hepatis, gallstones, inflammation of the bile ducts, narrowing of the bile ducts from scarring, injury from gallbladder surgery, tumours of the bile ducts or pancreas, tumours that have spread to the biliary system, etc.
8)Cirrhosis: Though it is an irreversible pathology of liver, symptoms are well managed and quality of life can be improved with homeopathy remedies

Diabetes (medically known as diabetes mellitus) is the name given to disorders in which the body has trouble regulating its blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels.
Diabetes can go silently undetected for a long time without symptoms. Many people first become aware that they have diabetes when they develop one of its potentially life-threatening complications, such as heart disease, blindness or nerve disease. Fortunately, diabetes can be managed with proper care. Diabetes is a chronic (life-long) condition that can have serious consequences. However, with careful attention to your blood sugar control, lifestyle modifications and medications, you can manage your diabetes and may avoid many of the problems associated with the disease.
There are three types of diabetes:
Type 1
Type 2
Gestational Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a disease that starts when the pancreas stops making insulin. Insulin lets blood sugar also called glucose enters the body’s cells to be used for energy. Without insulin, the cells can’t get the sugar they need and too much sugar builds up in the blood.
Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong disease that happens when the cells of the body can’t use insulin the right way or when the pancreas can’t make enough insulin. Insulin lets blood sugar also called glucose enters the body’s cells to be used for energy. When insulin is not able to do its job, the cells can’t get the sugar they need, and too much sugar builds up in the blood. Over time, this extra sugar in the blood can damage your eyes, heart, blood vessels, nerves, and kidneys.
Gestational diabetes is a temporary form of insulin resistance that usually occurs halfway through a pregnancy as a result of excessive hormone production in the body, or the pancreas’ inability to make the additional insulin that is needed during some pregnancies in women without a previous history of type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy, but women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk for later developing type 2 diabetes. Researchers have identified a small percentage of diabetes cases that result from specific genetic syndromes, surgery, chemicals, drugs, malnutrition, infections, viruses and other illnesses.
Heart disease and stroke approximately 75 percent of people with diabetes will die of heart disease or stroke, and they are likely to die at a younger age than people who do not have diabetes. People with diabetes have the same cardiovascular risk as if they have already had a heart attack. People with diabetes are two to four times more likely to have heart disease (more than 77,000 deaths due to heart disease annually). Heart disease death rates are also two to four times as high as adults without diabetes. People with diabetes are two to four times more likely to suffer a stroke. Blindness due to diabetic retinopathy each year 12,000 to 24,000 people lose their sight because of diabetes. Diabetes is the leading cause of new blindness in people 20 to 74 years of age.
Ten to 21 percent of all people with diabetes develop kidney disease. Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease (kidney failure), accounting for 43 percent of new cases. In 1999, 38,160 people with diabetes initiated treatment for end stage renal disease, and 114,478 people with diabetes underwent dialysis or kidney transplantation. Kidney failure requires the patient to undergo dialysis or a kidney transplant in order to live.
About 60 to 70 percent of people with diabetes have mild to severe forms of diabetes-related nerve damage, which can lead to lower limb amputations. In fact, diabetes is the most frequent cause of non-traumatic lower limb amputations. The risk of a leg amputation is 15 to 40 times greater for a person with diabetes. Each year, 82,000 people lose their foot or leg to diabetes.
Impotence afflicts approximately 13 percent of men who have type 1 diabetes and eight percent of men who have type 2 diabetes. It has been reported that men with diabetes, over the age of 50 have impotence rates as high as 50 to 60 percent.
Diabetes mellitus can be effectively managed with Electrohomeopathy treatment. Treatment in Electrohomeopathy is given at different levels. Electrohomeopathy can act as a preventive towards development of diabetes in patients who have a familial history of diabetes.
Electrohomeopathy can help patients who are on allopathic medication but their sugar levels are still beyond normal levels. In such cases Electrohomeopathy treatment started along with allopathic medication is found to give good results.
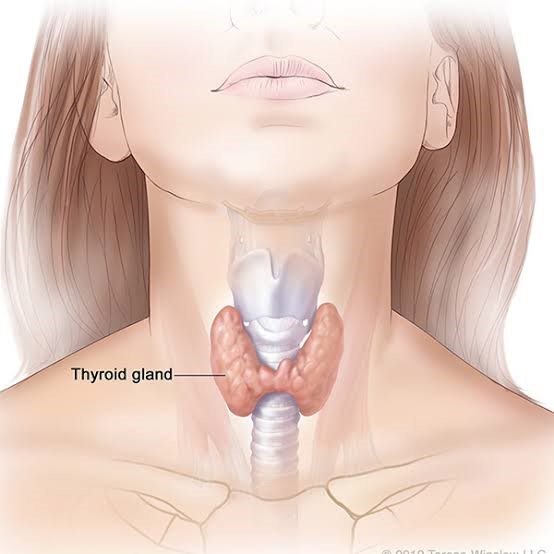
Hypothyroidism (also known as underactive thyroid) is a state in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. Since the main purpose of thyroid hormone is to “run the body’s metabolism”, it is understandable that people with this condition will have symptoms associated with a slow metabolism. Underactive thyroid is a very common medical condition and statistics suggest that 1 in 50 women and 1 in 1000 men will develop symptoms of hypothyroidism. It is more common in older women and can also occur more frequently during pregnancy.
Thyroid is a small butterfly shaped gland, in the front of the neck. The function of the thyroid gland is to convert iodine found in many foods into thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Only the thyroid gland has cells that can absorb iodine. The thyroid takes the iodine from foods, supplements and iodized salt and combines it with the amino acid tyrosine to produce T3 and T4. T3 and T4 travel throughout the body through the bloodstream and help cells convert oxygen and calories into energy. The pituitary gland produces the Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH). TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to produce more T3 and T4 hormones. If the levels of T3 and T4 thyroid hormones in the blood increase, the pituitary gland responds by reducing the production of TSH. The hypothalamus gland is located in the brain; it produces the TSH Releasing Hormone (TRH) which communicates with the pituitary gland which in turn stimulates the thyroid gland by producing and releasing TSH.
There are several potential diseases and conditions that can cause Hypothyroidism. Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of hypothyroidism worldwide. In iodine-replete individuals hypothyroidism is frequently caused by Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, or otherwise as a result of either an absent thyroid gland or a deficiency in stimulating hormones from the hypothalamus or pituitary.
1)Diet - The thyroid gland needs an array of nutrients to function optimally. Add essential fatty acids to your diet. Cold water fish such as salmon and cod as well as flaxseed, walnuts and almonds are great sources. Another option is to take a daily supplement such as fish oil. Seaweed, chlorella and algae should also be consumed frequently. They are rich in iodine and essential nutrients that maintain thyroid function balance.
Another important thing to keep in mind when it comes to a natural diet for hypothyroidism is that there are also foods that actually slow down thyroid function. These include broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, kale, spinach, turnips, soy, beans, and mustard greens. Also, take care to avoid overly processed food and limit dairy, sugar, artificial sweeteners, caffeine, and alcohol intake. Natural remedies and herbs can also be used to support optimal thyroid function.
2)Supplements of Vitamin C, E, Riboflavin, Zinc, Niacin, and pyridoxine might also help boost thyroid hormone Production.
3)Exercise – Aerobic exercise for 15 – 20 min a day is excellent for maintaining good thyroid function. It may boost the metabolism thus promoting good health.

The common cold is a viral infection of the lining of the nose, throat & chest. It is usually mild, with symptoms lasting about 1 week or less.
Flu is contracted in the same way that a cold is, a seasonal illness caused by a virus.
However both the cold and flu can share some similar symptoms, they are very different illnesses. The flu is much more serious than a cold. The flu virus is spread by coughing & sneezing. The cold & flu are both respiratory illness, but they are caused by different type of viruses. Flu symptom usually comes on quickly (within 3-6 hours) and consists of fever, body aches, dry cough and extreme tiredness. Cold symptoms are less severe and people experience a stuffy nose, productive cough, slight tiredness, and limited body ache.
Research shows that on an average, a person develops six to eight colds per year.
)Runny or stuffy nose
2)Sneezing & watery eyes
3)Irritation of the nasal lining
4)Itchy or sore throat
5)Cough & congestion
6)Mild headache
7)Nasal discharge which is initially watery but
8)later becomes thick yellow/green
9)Low grade fever with body ache
10)Hormonal changes like, hypothyroidism, during pregnancy or menses, etc.
11)Drugs like, Beta blockers, birth control pills, antihypertensive, sedatives, etc.
12)Anatomic defects like nasal polyps enlarge tonsils & adenoids, etc.
13)Emotional as well as physical stress.
1)Molds growing on dead leaves (fungus)
2)Airborne chemicals (chlorine & detergents)
3)Dust partials
4)Animal dander (skin flakes)
5)Droppings of cockroaches or household dust mites
6)Cigarette smoke
7)Frequent weather changes
8)Low immunity
9)Persistent exposure to infected individuals
Genetic factors - genetic factors are the major determinants of allergies. If both parents have allergic rhinitis or tendency to catch frequent cold. Then the patient`s risk of developing the same is 75%whereas if only one of them is allergic, the risk is 50%.
Age - Although most often allergic rhinitis may appear at any age. While an initial onset of the condition in early childhood decreases the possibility of its persistence in later life.
Other allergic conditions - eczema, food allergies, allergic asthma, etc. increases the risk.
Occupation - Persistence exposure to cold & certain allergens at workplace such as seed dust, wood dust, textile dust, animal dander, rubber latex, chemicals & storage mites.
Yes, although common cold & flu is generally mild and self-limiting that resolves in about 1-2 weeks, if any of the following sign and symptoms becomes evident, medical investigation becomes mandatory in order to prevent the development of any of the complications.
1)Fever of 103 degrees or higher accompanied by sweating, chills & cough
2)High fever accompanied by aches & fatigue, lasting more than 10 days
3)Vomiting & abdominal pain
4)Unusual sleepiness
5)Severe headache
6)Difficulty in breathing
7)Ear pain
8)Persistent cough with coloured phlegm
